AGC好题
因为我是从图论题单发现的所以就按图论思考了
先按套路 i→pi 连边,会构成若干个环
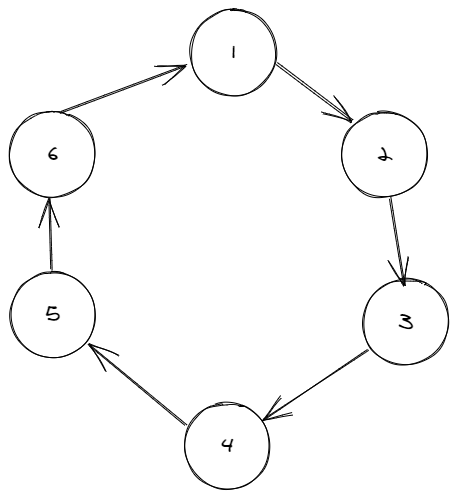
发现没啥能用的性质
然后 ai 的个很好的东西,因为 pi 要么是 ai 要么下一个是 ai 图上表示就类似
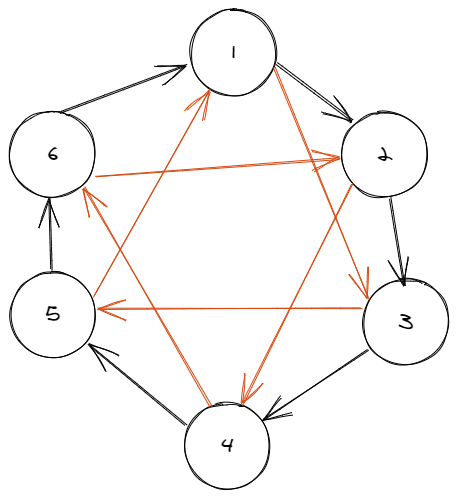
如果每个 pi=ai 都成立,那就是原图了
同样的每个 ppi=ai 都成立就是

这里需要讨论一下,环长位偶数的话像上图会把原图拆成两个大小为一半的环
如果是奇数则
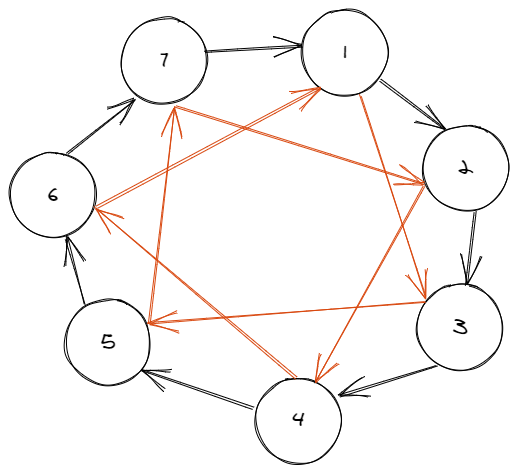
拉平看一下
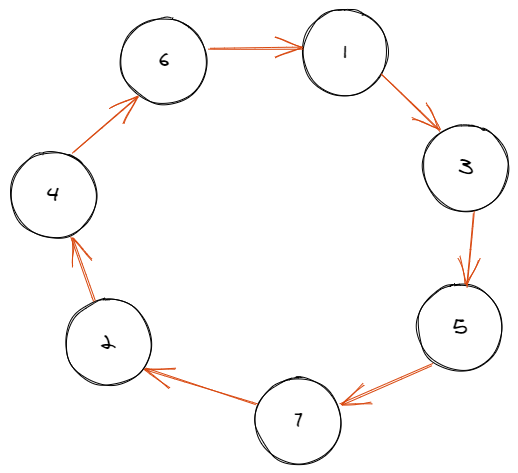
可以发现这个结构和原图是一样的
最后如果既有 pi=ai ppi=ai 就是
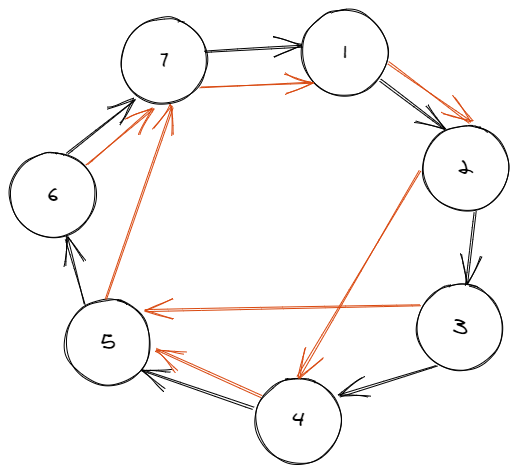
拉直
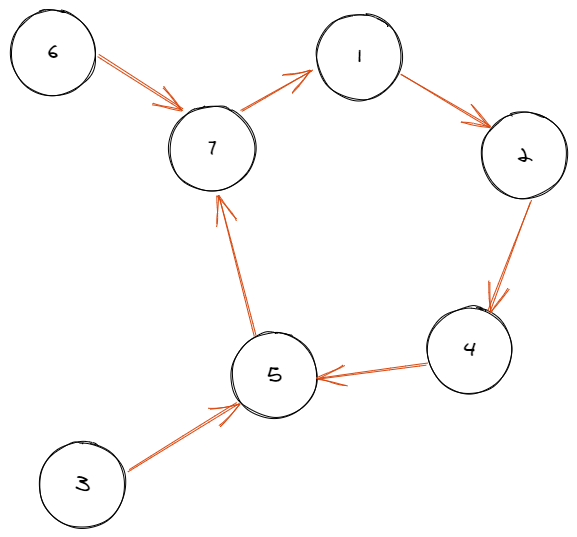
是一个内向基环树
现在我们拿到了变换完的 i→ai 的图,求原图的方案数
环和基环树没啥关系也不能相互作用
所以分别处理
环的部分考虑dp
dps,k 表示大小为 s 的环考虑到第 k 个,如果 s 是奇数那么可以有一个和原图同构的图和原图,即 dps,k−1+dps,k−1
同时也可以向上合并成大环,最后乘起来
基环树的部分
基环树上的链肯定是得压到环里的,对着图手玩一会就能发现
这个链长度为 l1 ,到下一个链长度为 l2
如果 l2<l1 必然塞不下
如果 l1=l2 刚刚好一种方案
否则的话第一个点隔一个点链和直接连有两种方案
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
| #include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n;
int a[N], in[N], st[N], top;
bool inst[N], vis[N], cyc[N];
int len[N];
void dfs(int x) {
if (vis[x]) {
if (inst[x]) {
for (int i = top; i >= 1; i--) {
cyc[st[i]] = 1;
if (st[i] == x) {
return;
}
}
}
return;
}
vis[x] = inst[x] = 1;
st[++top] = x;
dfs(a[x]);
inst[x] = 0;
}
int cnt[N];
ll ans = 1;
void pre(int x) {
int tot = 0, fr = 0, ed = 0, frid;
while (cyc[x]) {
++tot;
cyc[x] = 0;
if (len[x]) {
if (!fr) {
fr = tot;
ed = tot;
frid = x;
} else {
int pm = (len[x] < tot - ed) + (len[x] <= tot - ed);
ans = 1ll * ans * pm % mod;
ed = tot;
}
}
x = a[x];
}
if (!fr) {
++cnt[tot];
} else {
int kl = (len[frid] < tot - ed + fr) + (len[frid] <= tot - ed + fr);
ans = 1ll * ans * kl % mod;
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
++in[a[i]];
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i);
if (!in[i]) {
q.push(i);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if ((cyc[i] && in[i] > 2) || (!cyc[i] && in[i] > 1)) {
cout << 0;
exit(0);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
len[a[x]] = len[x] + 1;
if (!cyc[a[x]]) {
q.push(a[x]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (cyc[i]) {
pre(i);
}
}
static ll num[N];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (cnt[i]) {
num[0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= cnt[i]; j++) {
if (i > 1 && i % 2 != 0) {
num[j] = (num[j - 1] + num[j - 1]) % mod;
} else {
num[j] = num[j - 1];
}
if (j > 1) {
num[j] =
(1ll * num[j] + 1ll * num[j - 2] * 1ll * (j - 1ll) %
mod * 1ll * i % mod) %
mod;
}
}
ans = 1ll * ans * num[cnt[i]] % mod;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
|






